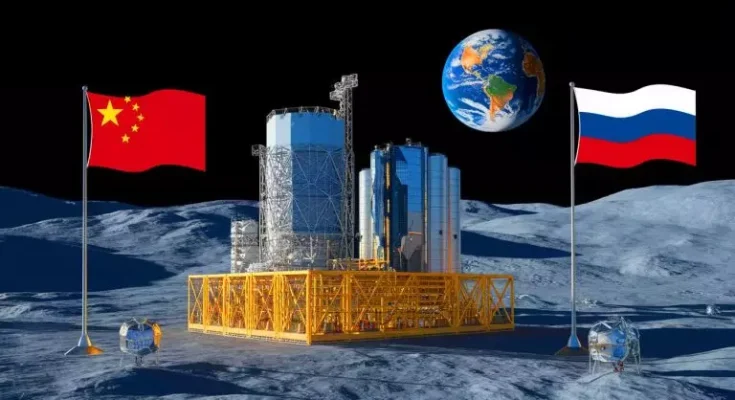
Plans to establish a nuclear reactor on the Moon have been officially confirmed, sparking considerable surprise in the United States. Though it may sound like a concept from a futuristic science fiction film, this project is a very real initiative spearheaded by China. The country is working towards the construction of a nuclear plant on the Moon, which is intended to support a more permanent research station in collaboration with Russia.
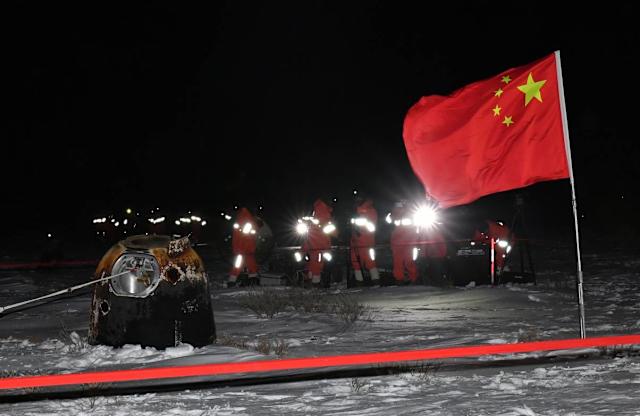

This ambitious plan was unveiled during a presentation in Shanghai, where foreign governments and organizations were briefed on the International Lunar Research Station (ILRS). The mission’s Chief Engineer, Pei Zhaoyu, outlined how the Moon’s energy requirements could be met using large-scale solar arrays, along with pipelines and cables for heating and electricity that would be constructed on the lunar surface. This nuclear facility is slated for completion by 2035, with China aiming to land its astronauts on the Moon within the next five years.
The project sets China in direct competition with the United States, which also plans to return astronauts to the Moon within the next two years. This renewed space race echoes the original lunar exploration rivalry between the two nations that began over six decades ago.
The notion of a nuclear plant on the Moon was endorsed by Russia’s space agency, Roscosmos, in 2024. The agency announced plans to build a nuclear reactor on the lunar surface in partnership with China’s space administration, the CNSA, in order to power the ILRS. This partnership highlights Russia’s leadership in nuclear power technology, especially in the context of space exploration, as noted by Wu Weiren, the chief designer of China’s lunar exploration program.

Additionally, Russia is collaborating with China on a nuclear-powered cargo spaceship, which has been described as a “space tugboat.” Yury Borisov, the former head of Roscosmos, detailed that this massive structure would use a nuclear reactor and high-power turbines to transport large cargo between orbits, collect space debris, and serve other functions in space exploration.